What is Sebum on Scalp? Affects and Benefits
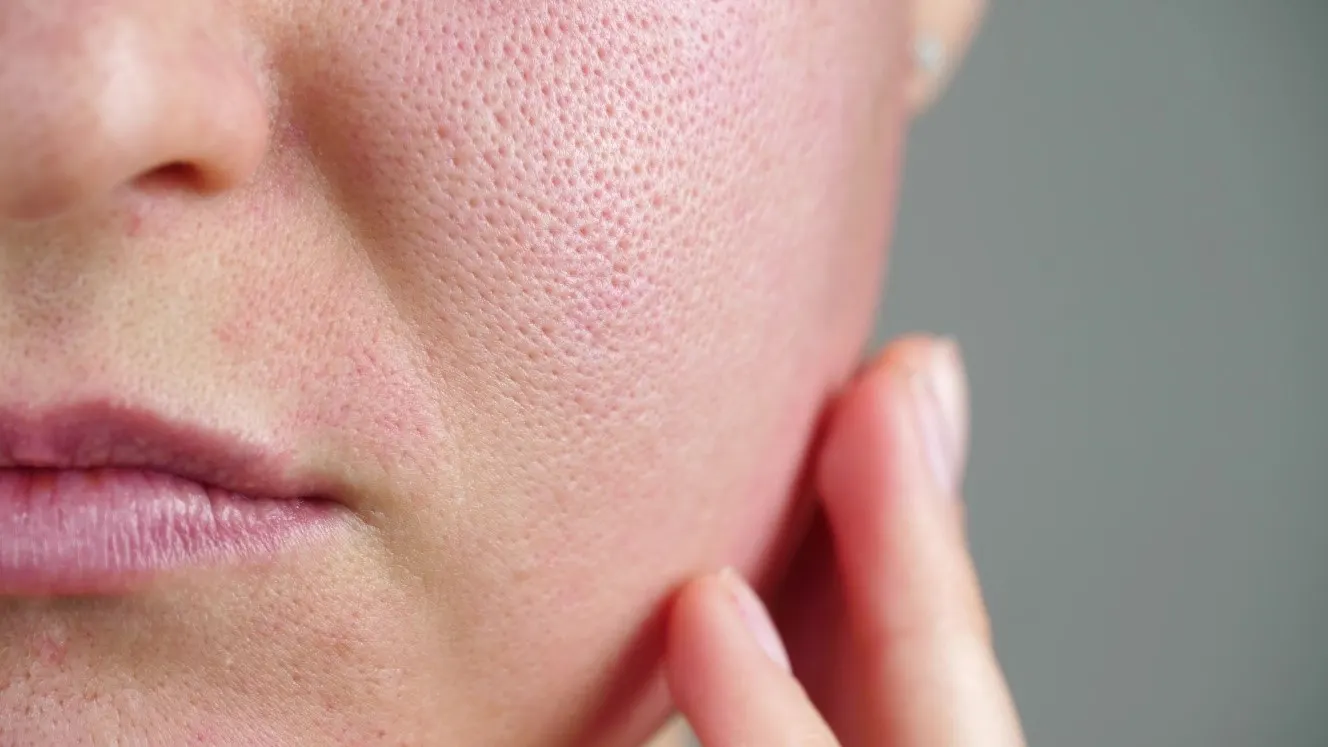
When it comes to oily skin or oily hair, the root source is Sebum. This is a waxy, oil like substance that is secreted all over the body and forms the first line of protection for your largest organ – the skin.
Sebum is produced by sebaceous glands that are found in the upper layers of your skin. They generally accompany hair follicles, which help in the distribution of the sebum on your skin. Sebum is made up of fatty acids, triglycerides, sugars, cholesterol like lipids, wax, and other organic compounds.
Although sebaceous glands are found all over, the largest concentration is on the most sensitive areas of your body - the face and the scalp. These glands produce sebum via holocrine secretion, where the sebum is produced in a sac like structure. The enclosing plasma membrane eventually ruptures and allows for the sebum to flow into the hair follicles. This in turn allows the oil to spread across the skin.
But what is the point of sebum?
Your body produces sebum to create a protective layer on your skin. The sebum lubricates and moisturises, creating a barrier to prevent the escape of excess moisture. It safeguards you from pollution or any external harmful elements, including UV rays from the sun. Sebum also guards against any friction that can cause harm to your skin.
It transports Vitamin E to the skin, lending it antioxidant properties that reduce oxidative stress on your skin and hair. Sebum also coats your hair in a thin layer that prevents it from drying out. When there is not enough sebum on hair, the cuticle opens and allows the moisture to escape. This can lead to frizzy hair, breakage, and split ends.
A major aspect of sebum is that it acts as an anti-fungal and anti-bacterial shield that protects against infections and harmful microbes. But this can be a double-edged sword, as excess oil can cause you other forms of ailments.
What happens if there is a fluctuation in sebum?
Although sebum is there to protect you, it can also cause you a bit of trouble. If excess sebum is produced by your scalp and face, it can lead to oily and greasy skin which is prone to acne. You might notice blackheads or whiteheads appearing on your skin, including on your scalp. This is due to blocked and inflamed pores that can further worsen the sebum buildup on scalp.
Excess sebum on scalp and hair can also lead to the worst of your scalp troubles – dandruff. Sebum on scalp is the primary cause of dandruff when combined with the fungus, Malassezia Globosa. This fungus breaks down the sebum on scalp and creates by-products that are reactive to half the people in the world. They breakout into severe itching, redness, and white flakes of dead skin cells. Many people even try dandruff home remedies to help them find an answer on how to get rid of dandruff. But for quicker results you should try the Head and Shoulders Neem shampoo that helps to get rid of the dandruff causing germs. The effect of excess sebum on hair is quite stark, as blocked pores can lead to thinning of your hair, and in extreme cases even hair loss.
The flipside of excess sebum is inadequate sebum production. This can lead to drying out of your scalp and hair, which leads to a flaky scalp that is prone to damage and itching. This can be easily managed by moisturisers and the use of dry scalp conditioners like the Head and Shoulders Supreme Scalp Rejuvenation with Argan oil.
What affects sebum production?
Sebum production can fluctuate quite a bit, and you might have noticed that some days you have oily skin and some days it’s completely dry. But what controls it?
-
Hormonal changes –
This is the main regulator of your sebum production. Any fluctuations in your hormones can spike your sebum levels or completely cut them. This is something you can’t really control but can try to manage. For example, stress releases hormones that play havoc on your sebum levels. So, if you reduce your stress, it should control your sebum production. -
Age –
Since hormones have such a large part to play with sebum production, age is a big factor as well. When you’re going through puberty, your hormones are all over the place and thus you see a breakout of acne. The older you get, the less impact your hormones have on the sebum production, especially for women after menopause. -
Weather changes –
This sounds unrealistic, but changes in the climate can affect your oil production. The body produces oil based on certain triggers. So, if it’s a cold climate, your body might produce more oil to trap the moisture. If it’s hot, the body might react in a different way. -
Malnutrition –
What you put inside your body is what determines how it reacts, this should be obvious to you. Studies have shown that consumption of high dietary fat and carbohydrates directly leads to an increase in sebum production. -
Hygiene –
If you don’t wash your hair often, it can lead to a buildup of sebum on your scalp. This can lead to blocked pores, white heads, and infections, which sends a message to your body to produce less oil. If your scalp is excessively dry and you don’t use moisturisers, it can trigger your body into producing even more sebum and disrupting your scalp sebum control. Wash regularly with good products like the Head and Shoulders 2 in 1 Cool Menthol shampoo and conditioner to avoid this. -
Circadian rhythm –
Your body functions on a clock like every other human being. When this natural rhythm is disturbed, your body can respond in different ways. Poor sleep patterns are the most common disruptors of your circadian clock and can possibly lead to a disruption in your sebum production.
Sebum is a natural occurrence which is vital in the proper functioning of your body. And any change in this process can cause a bit of trouble for you. It is thus important to understand why there is sebum on hair or on face or on any part of your body.



